Archive
The Sound and Style of Consciousness
In music, timbre also known as tone color or tone quality from psychoacoustics, is the quality of a musical note or sound or tone that distinguishes different types of sound production, such as voices and musical instruments, string instruments, wind instruments, and percussion instruments. The physical characteristics of sound that determine the perception of timbre include spectrum and envelope.
a signal with its envelope marked in red
What I remember from my 7th grade general music class about timbre is that it is what made modern pop and rock different from other forms of music. All of those sound effects that become possible with electric amplification allow us to transform the same kinds of melodies that have always been a part of music into new kinds of sonic textures. Any song can be made into a heavy metal or punk song by cranking up the amplitude and distortion and manipulating the tempo.
The Wiki gives a list of subjective experiences and objective acoustic properties, such as:
Subjective Objective
Vibrato Frequency modulation
Tremolo Amplitude modulation
I think that this a clue that timbre can be used meaningfully as a jumping off point for understanding subjectivity and consciousness. If we think of the red signal envelope as a cross section of a 3D prismatic glacier behind it, the axis of that figurative third dimension would be where private significance (aesthetic quality) intersects public spacetime.
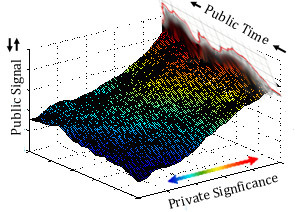
I’m not saying that qualia can literally be reduced to a kind of perpendicular meta-spacetime, but that it can be figuratively thought to cast a shadow which is measurable in those terms. The public universe is flat in comparison to the private universe, even though any particular private experience of eternity is of course orders of magnitude narrower than the totality of all experience. The full extent of our own lives and the lives of others is hidden by the constraint of our insensitivity. Our attention is directed to public facing events, to places and times outside of our private here and now.
Timbre at least recognizes the dipole of subjective and objective dimensions of phenomena and the sensible link between them. Our Western approach of psychoacoustics still reduces the subjective psycho- qualities to a mechanical model which is presumed to be driven by the acoustics only, but what I suggest is that acoustic mechanics are themselves micro-aesthetic experiences which are shared on all phenomenal levels (sub-personal, personal, and super-personal).
Timbre is a word which has been called “the psychoacoustician’s multidimensional waste-basket category for everything that cannot be labeled pitch or loudness”. The difference between a recording of a flute and a recording of a guitar playing the same song could be described in terms of timbre. Each instrument has its own idiosyncratic mixture of tonal and extra-tonal noise-like qualities. When we talk about playing a song on the piano, we are treating the melody as the object. What is being played is an abstract concept of sequenced notes, but what is bringing that abstraction into a concretely realized experience is the acoustic and artistic qualities of the instrument and the performance.
A font or typeface can be seen in a similar way. The invention of customizable fonts was one of the favorite features of early word processors. Instead of being locked into a particular typewriters look, the consumer could now make their printed output look more like published text. Font designers had to painstakingly build the look of each letter in the character set (since a computer would not be much good at guessing what a Helvetica style might be). Soon the entire typographic palette of styles and sizes were available, bringing into sharp distinction the difference between the alphanumeric data (ASCII text), and the font (character set). We can understand, that just as the melody of a song sounds different when it is played on a flute than when it is blasting out of a distorted electric guitar, a phrase written in Times New Roman carries a different meaning when it is written in Comic Sans. The computer, however, does not have any need to differentiate. It doesn’t care what font you write a program in, just as sheet music doesn’t carry instructions for a flute to sound like a flute.
If we use timbre and typeface as metaphors for qualia, we can see how it describes a difference in kind from the skeletal underpinnings of quanta. It’s true that we can use quantitative mechanisms to communicate qualia, but only if the receiver has the right kind of sensory range to match the sender’s intent. The mechanism has no way to appreciate the aesthetic content though, as all such qualities, whether they are fonts, timbre, image, or meaning, are reduced to the same binary digits. Compare this with what we hear, for example, when dragging a stick along the ground. There is the sound of the foot of the stick scraping the ground itself, and then there is the amplified, woody resonance which describes the length, mass, and density of the stick. Both can be felt as well as heard. The effect overall is a unified gestalt. Unlike a computation in which data must be explicitly separated and handled differently (some bits belong to the font, some to the text), natural sound is a feeling for our body and a knowing for our mind that is bound together metaphorically.
There is no mechanical process through which feelings and thoughts are bound. Instead, they are divided, like the spectrum of visible light is divided from white light, from the common sense of all experience. There is no way to simulate that coherence mechanically, but given enough artificial cues, our naturally poetic psyche will confabulate animation into it. We look at the words typed in a romantic script font and get a sense of a voice which might make the words seem pretentious or anachronistic. We hear the distorted guitar strings and feel that the song has become massively and explosively energetic. The ‘information’ which describes the underlying structure of the music or the typeface is non-poetic. It is only pixels and mathematical relations which relate to themselves and to mathematics in general, not to the experience of being alive. For being alive and aware, we need extra-mathematical qualities – the same qualities from which math itself emerges.
“There is no information without representation”
My rebuttal to this from New Empiricism
Information is one of the most poorly defined terms in philosophy but it is a well defined concept in physical theory. How can it be that a clear idea in one branch of knowledge can be murky in another?
The physical meaning of information is succinctly summarised in the Wikibook on “Consciousness Studies”:
“The number of distinguishable states that a system can possess is the amount of information that can be encoded by the system.”
In most cases a “state of a system” boils down to arrangements of objects, either material objects laid out in the world or sequences of objects such as the succession of signals in a telephone line. So information is represented by physical things laid out in space and time. There is no information without this representation as an arrangement of physical objects.
Information can be processed by machines. As an example, computers use the “distinguishable states” of charge in electrical components to perform a host of useful tasks. They use the state of electrical charge in electronic components because charge can be manipulated rapidly and can be impressed on tiny components, however, computers could use the states of steel balls in boxes or carrots flowing on conveyor belts to achieve the same effect, albeit more slowly. There is nothing special about electronic computers beyond their speed, complexity and compactness. They are just machines that contain three dimensional arrangements of matter.
Philosophers use information in a much less well-defined fashion. Philosophical information is far more fuzzy and involves the quality of things such as hardness or blueness. So how does philosophical blueness differ from a physical information state?
Physical information about the world is a generalised state change that is related to particular events in the world and could be impressed on any substrate such as steel balls etc.. This allows information to be transmitted from place to place. As an example, a heat sensor in England could trigger a switch that opens a trapdoor that drops a ball that is monitored on a camera that causes changes in charge patterns in a computer that are transmitted as sounds on a radio in the USA. If the sound on the radio makes a cat jump and knock over a vase then it is probably valid to look at the vase and say “its hot in England”. So physical information is related to its source by the causal chain of preceding steps. Notice that each of these steps is a physical event so there is no information without representation as a state in the real world.
In the philosophical idea of information “hot” or “cold” are particular states in the mind. Our mental states are not uniquely related to the state of the world outside our bodies. As an example, human heat sensors are fickle so a blindfolded person might contain the state called “cold” when their hand is placed in water at 60 degrees or ice water at zero degrees. Our “cold” is subjective and does not have a fixed reference point in the world. Our own information is a particular state that could be induced by a variety of events in the world whereas physical information can be a variety of states triggered by a particular event in the world.
To summarise, information in physics is a state change in any substrate. It can be related to the state change in another substrate if a causal chain exists between the two substrates. Information in the mind is the state of the particular substrate that forms your particular mind.
Your mind is a state of a particular substrate but a “state” is an arrangement of events. The crucial questions for the scientist are “what events?” and “how many independent directions can be used for arranging these events?”. We can tell from our experience that at least four independent axes (or “dimensions”) are involved.
Note
The fact that there is no information without representation of the information as a physical state means that peculiar non-physical claims such as Cartesian Dualism and Dennett’s “logical space” are not credible.
Daniel C Dennett. (1991). Consciousness Explained. Little, Brown & Co. USA. Available as a Penguin Book.
Dennett says: “So we do have a way of making sense of the idea of phenomenal space – as a logical space. This is a space into which or in which nothing is literally projected; its properties are simply constituted by the beliefs of the (heterophenomenological) subject.” Dennett is wrong because if the space contains information then it must be instantiated as a physical entity, if it is not instantiated then it does not exist and Dennett is simply denying the experience that we all share to avoid explaining it. Either we have simultaneous events or are just a single point, if we have simultaneous events the space of our experience exists.
“So information is represented by physical things laid out in space and time.”
Why would physical things ‘represent’ anything though? Without some sensory interpretation that groups such things together so that they appear “laid out in space and time”, who is to say that there could be any ‘informing’ going on?
“computers use the “distinguishable states” of charge in electrical components to perform a host of useful tasks.”
Useful to whom? The beads of an abacus can be manipulated into states which are distinguishable by the user, but there is no reason to assume that this informs the beads, or the physical material that the beads are made of. Computers do not compute to serve their own sense or motives, they are blind, low level reflectors of extrinsically introduced conditions.
“Your mind is a state of a particular substrate but a “state” is an arrangement of events. ”
States and arrangements are not physical because they require a mode of interpretation which is qualitative and aesthetic. Just as there can be no disembodied information, there can be no ‘states’ or ‘arrangements’ which are disentangled from the totality of sensible relations, and from specific participatory subsets therein. Information is a ghost – an impostor which reflects this totality in a narrow quantitative sense which is eternal but metaphysical, and a physical sense which is tangible and present but in which all aesthetic qualities are reduced to a one dimensional schema of coordinate permutation. Neither information nor physics can relate to each other or represent anything by themselves. It is my view that we should flip the entire assumption of forms and functions as primitively real around, so that they are instead derived from a more fundamental capacity to appreciate sensory affects and participate in motivated effects. The primordial character of the universe can only be, in my view metaphenomenal, with physics, information, and subjectivity as sensible partitions of the whole.
Seeing Visibility
Given that light has many strange properties, both on our natural scale as rays and on the elementary scale as photons, there is every reason to doubt that light qualifies as something which is unambiguously physical. On the other hand, since we cannot imagine a completely new color wheel, it would seem to say that the experience of seeing light is “real”, and not, a label for certain kinds of information that is fabricated in the brain. People who become blind at an early age, for example, experience stimulation to their visual cortex as tactile stimulation rather than seeing lights or spots.The condition of blindsight shows that parts of our brain can receive optical information without our having experienced that information personally as visual sensation.
In a way, white light can be considered to be what it looks like when transparency is concentrated. White light is when the quality of visibility is so saturated that it exceeds the range of discernment . A bright light illuminates a room not with whiteness but with clarity. To shed light on something is to flood the visual field with an immediacy of aesthetic acquaintance that suggests veridical qualities of the environment being illuminated. This is why we have metaphors such as ‘seeing the light’. Because it is about being connected with the presence of what is true and sensible, rather than being passively bombarded with particles. It can be said that our experience of seeing is not a direct detection of what is true, since there are so many ways to reveal optical illusion.
By calling it an illusion, we are framing the phenomena in a way as to implicate human fallibility rather than physics. Somehow we are wrong about what our eyes report, yet it is not clear that our assumption about what our eyes are reporting is scientifically valid. In fact, if it were not for these optical illusions, science would have very little to go on in determining the nature of vision as separate from physical truth, so it is actually the gaps between our expectations and the truth which reveal more truth, both about the nature of visual awareness, optics, electromagnetism, and quantum mechanics. Optical illusions are an encyclopedia of the nature of perceptual illusion, physical reality, and the relation between the two.
The folk science explanation for light perception generally begins with the idea that we can see light hitting our retina. That may be true, but not scientifically. The part that light plays in our visual system ends with the isomerization of rhodopsin in the retina. If what we see as “light” is in the visual cortex, then obviously what the visual cortex receives is not photons from the outside world, and it is not a direct analog that shows up as a small screen of images in an MRI. To even guess at some of the content of our visual field requires a blind statistical reconstruction. There is no plain-text transmission of images in our brain to simply hack into and view.
The effect that light has on the retina is merely to trigger the geometric extension of Vitamin A molecules and stop the flow of glutamate to the bipolar cells. That is well behind the first ganglion that would lead to the optic nerve and visual cortex. I propose instead that photons are not entities that are independent of their transmitters and receivers, and that light is therefore not physical but rather inter-physical, aka, phenomenal, aka sensory. Photons are measures of the sensitivity of our mode of detection. It is neither ray, beam, particle, or wave, but rather a rhythmic phenomenalization of matter – a feeling that matter has about what is going on around it. By making inferences beyond our sensible grasp, I think that Quantum Theory has given noun and verb-like properties to what are ultimately adjectives. Bosons and fermions may not be like that at all, but rather they are opportunities for matter to re-acquaint itself. The elementary measurable features of the cosmos may not be particles or strings, but qualities which characterize the capacity of matter to measure and interact with itself. Physics is a mirror. For every action and equal and opposite reaction, because equal and opposite reaction is a perfect reflection of our mode of scientific inquiry. We are investing our coins of empiricism in nature, extracting the empirical value, and recording the profit in our scientific ledger, like good, serious 18th century gentlemen.
It seems to me that only a medium which is intrinsically filled with the sense of color, form, and intensity across the many physical scales could reliably and veridically bridge the gap between public material realism private experience.The notion of a seeing light as a Rube Goldberg patchwork of conveyance into separate effects on every level*, all transported through a one dimensional collision detection schema is not consistent with reality. There are too many examples of people who have seen things in dreams and visions, too many qualities of visual experience which cannot be decomposed sensibly to pixels or lines for the photon explanation to be satisfactory. The qualia of color alone, whose idiopathic shifts and wheel-like symmetry have no place in the smooth continuum of the electromagnetic spectrum.
I suggest that light is only one specific form of a more universal medium, and that this medium is already known to us informally by the word ‘sense’. Sense as in sensation, sensitivity, sensor, but also as in making sense, sixth sense, and ‘in the sense of’. The unity of all sense can be more precisely expressed as ‘primordial identity pansensitivity’, ‘nested sensory-motive participation’, or even something like ‘self-tesselating aesthetic re-aquaintence’, depending on how technical and pretentious we want to get. From this Absolute firmament, and I think only from this firmament, can we get the full range of private experience, public physics, symbolic information, and the capacity to compare and contrast them. Only when physics is seen as identical with sense can physics be completed.
On the elementary level, with a nested sense primitive, we get relativistic locality (so eigenmetrics rather than eigenstates). Sense is modulating its own self-transparency and reflectivity to generate eigenmetric milieus – levels of scale that foster certain kinds of aesthetic themes and activities. The micro-world with its mathematical-molecular-insectoid clarity is different from the soft, lush features of zoological-arboreal-botanical existence. On some level perhaps, sense is nearly undiluted, and so the entire history of the cosmos is as a single now – a white whole singularity in which the now cannot even be completed and the here cannot hold even the hint of a ‘there’. On that level, there is non-locality.
*optical, molecular, cellular, ocular, neurological, psychological, sociological, zoological..
The Sense of Acquaintance
In David Chalmers’ Precis of The Conscious Mind, in the summary of his argument for the Paradox of Phenomenal Judgment, he uses a particular wording that caught my attention:
“Knowledge of and reference to phenomenal states is based on something tighter than a causal relation; it is based on a relation of acquaintance.”
The term acquaintance sheds some new light on the idea of sense. While he uses it to pull away from functionalist assumptions, I would argue that he needs to go further still, so that there can be no confusion that acquaintance could be accomplished without an aesthetic appreciation. The question of whether an aesthetic quality can be appreciated mechanically, or if mechanism is inherently and eternally anesthetic is at the heart of all philosophical debate over consciousness and artificial intelligence.
In a related metaphysical question, can it be said that sense is truly an acquaintance, or is it always ultimately a re-acquaintance on a deeper level? Each of us, for example, had a moment when their eyes first showed them color. Of course, this would not have been possible had our eyes themselves not been expecting to fulfill a history of acquaintance with light discernment throughout the history of biology, and perhaps even biochemistry and electromagnetism itself. By contrast, our eyes do not acquaint us personally with X-Rays or radio waves. This suggests that on some level, acquaintance may be impossible if it is not ultimately a re-acquaintance.
Any understanding of sense should include this kind of holographic chicken-and-egg paradox of the expected and the unexpected. In order to support novelty in communication, there must be a common agreement on the fundamentals that comprise the channel of communication – its alphabet, protocols, the bandwidth specifications, etc. Each layer of varying information can be seen to arise from a deeper layer of invariant information, but ultimately, the capacity for sense to bootstrap itself must dissolve the difference between acquaintance and re-acquaintance. Sense is beneath time and novelty, beneath difference and similarity. It is (or ‘this is’) eternal by necessity, but it is also eternally masking itself into temporary dis-acquaintance.
Analogue, Brain Simulation Thread
Tell the difference between a set of algorithm’s in code that can mimic all the known processes for the input and output of a guitar into analogue equipment. The answer is no, because pros cant tell the difference. The entire analogue process has been sufficiently well modeled and encapsulated in the algorithmns. The inputs and outputs are physically realistic where the input and output are important. That is what substrate modelling of brain processes in computational neuroscience is about. i.e. Brain simulations.
Just because our analysis of what is going on in the brain reminds is of information processing does not mean that the brain is only an information processor, or that consciousness is conjured into existence as a kind of information-theoretic exhaust from the manipulation of bits.
What you are not considering is that beneath any mechanical or theoretical process (which is all that computation is as far as we know) is an intrinsic sensible-physical context which allows switches to load, store, and compare – allows recursive enumeration, digital identities,…a whole slew of rules about how generic functions work. This is already a low level kind of consciousness. That could still support Strong AI in theory, because bits being the tips of an iceberg of arithmetic awareness would make it natural to presume that low level awareness scales up neatly to high level awareness.
In practice, however, this does not have to be the case, and in fact what we see thus far is the opposite. The universally impersonal and uncanny nature of all artificial systems suggests the complete lack of personal presence. Regardless of how sophisticated the simulation, all imitations have some level at which some detector cannot be fooled. Consciousness itself however, like the wetness of water, cannot be fooled. No doll, puppet, or machine which is constructed from the outside in has any claim on sentience at the level which we have projected onto it. This is not about a substitution level, it is about the specific nature of sense being grounded in the unprecedented, genuine, simple, proprietary, and absolute rather than the opposite (probabilistic, reproducible, complex, generic, and local). From the low level to a high is not a difference in degree, but a difference in kind, even though the difference between the high level and low level is a difference in degree.
What I mean by that is that anything can be counted, but numbers cannot be reconstructed into what has been counted. I count my fingers…1, 2, 3, 4, 5. We have now destructively compressed the “information” of my hand, each unique finger and the thumb, into a figure. Five. Five can apply generically to anything, so we cannot imagine that five contains the recipe for fingers. This is obviously a reductio ad absurdum, but I introduce it not as a straw man but as a clear, simple illustration of the difference between sensory-motive realism and information-theoretic abstractions. You can map a territory, but you can’t make a territory out of a map regardless of how much the map reminds you of the territory.
So yes, digital representations can seem exactly like analog representations to us, but they are both representations within a sensory context rather than a sensory-motive presentation of their own. All forms of representation exist to communicate across space and time, bridging or eliding the entropic gaps in direct experience. It’s not a bad thing that modeling a brain will not result in a human consciousness, its a great thing. If it were not, it would be criminal to subject living beings to the horrors of being developed and enslaved in a lab. Fortunately, by modeling these beautiful 4-D dynamic sculptures of the recordings of our consciousness, we can tap into something very new and different from ourselves, but without being a threat to us (unless we take it for granted that they have true understanding, then we’re screwed).



Recent Comments